Core¶
Overview¶
stoQ is an extremely flexible framework. In this section we will go over some of the most advanced uses and show examples of how it can be used as a framework.
Framework¶
stoQ is much more than simply a command to be run. First and foremost, stoQ is a framework. The command stoq is simply a means of interacting with the framework. For more detailed and robust information on APIs available for stoQ, please check out the plugin documentation.
Stoq is the primary class for interacting with stoQ and its plugins.
All arguments, except for plugins to be used, must be defined upon instantiation.
Plugins can be loaded at any time. However, to ensure consistent
behavior, it is recommended that all required plugins be loaded
upon instantiation.
For these examples, it is assumed the below plugins have been installed in $CWD/plugins:
- dirmon
- exif
- filedir
- hash
- yara
Individual Scan¶
Individual scans are useful for scanning single payloads at a time. The user is
responsible for ensuring a payload is passed to the Stoq class.
Note
Provider plugins are ignored when conducting an individual scan.
First, import the required class:
>>> from stoq import Stoq, RequestMeta
We will now define the plugins we want to use. In this case, we will be loading the
hash, andexifplugins:>>> workers = ['hash', 'exif']
Now that we have our environment defined, lets instantiate the
Stoqclass:>>> s = Stoq(always_dispatch=workers)
We can now load a payload, and scan it individually with stoQ:
>>> src = '/tmp/bad.exe' >>> with open(src, 'rb') as src_payload: ... meta = RequestMeta(extra_data={'filename': src}) ... results = s.scan( ... content=src_payload.read(), ... request_meta=meta) >>> print(results) ... { ... "time": "...", ... "results": [ ... { ... "payload_id": "...", ... "size": 507904, ... "payload_meta": { ... "should_archive": true, ... "extra_data": { ... "filename": "/tmp/bad.exe" ... }, ... "dispatch_to": [] ... }, ... "workers": [ ... { ... "hash": { ... [...]
Using Providers¶
Using stoQ with providers allows for the scanning of multiple payloads from multiple sources. This method will instantiate a Queue which payloads are published to for scanning by stoQ. Additionally, payloads may be retrieved from multiple disparate data sources using Archiver plugins.
First, import the required class:
>>> from stoq import Stoq
We will now define the plugins we want to use. In this case, we will be loading the
dirmon,filedir,hash, andexifplugins. We will also set thebase_dirto a specific directory. Additionally, we will also set some plugin options to ensure the plugins are operating the way we’d like them:>>> always_dispatch = ['hash'] >>> providers = ['dirmon'] >>> connectors = ['filedir'] >>> dispatchers = ['yara'] >>> plugin_opts = { ... 'dirmon': {'source_dir': '/tmp/datadump'}, ... 'filedir': {'results_dir': '/tmp/stoq-results'} ... } >>> base_dir = '/usr/local/stoq' >>> plugin_dirs = ['/opt/plugins']
Note
Any plugin options available in the plugin’s .stoq configuration
file can be set via the plugin_opts argument.
3. Now that we have our environment defined, lets instantiate the Stoq class,
and run:
>>> s = Stoq(
... base_dir=base_dir,
... plugin_dir_list=plugin_dirs,
... dispatchers=dispatchers,
... providers=providers,
... connectors=connectors,
... plugins_opts=plugins_opts,
... always_dispatch=always_dispatch
... )
>>> s.run()
- A few things are happening here:
- The
/tmp/datadumpdirectory is being monitored for newly created files - Each file is opened, and the payload is loaded into
Stoq - The payload is scanned with the
yaradispatcher plugin - The yara dispatcher plugin returns a list of plugins that the payload should be scanned with
- The plugins identified by the
yaradispatcher are loaded, and the payload is sent to them - Each payload will always be sent to the
hashplugin because it was defined inalways_dispatch - The results from all plugins are collected, and sent to the
filedirconnector plugin - The
filedirplugin saves each result to disk in/tmp/stoq-results
- The
Manual Interaction¶
Stoq may also be interacted with manually, rather than relying on the normal workflow.
In this section, we will touch on how this can be done.
Instantiating stoQ¶
Let’s start by simply instantiating Stoq with no options. There are several arguments
available when instantiating Stoq, please refer to the plugin documentation
for more information and options available.:
>>> from stoq import Stoq
>>> s = Stoq()
Loading plugins¶
stoQ plugins can be loaded using a simple helper function. The framework will
automatically detect the type of plugin is it based on the class of the plugin.
There is no need to define the plugin type, stoQ will handle that once it is loaded.:
>>> plugin = s.load_plugin('yara')
Instantiate Payload Object¶
In order to scan a payload, a Payload object must first be instantiated. The
Payload object houses all information related to a payload, to include the
content of the payload and metadata (i.e., size, originating plugin information,
dispatch metadata, among others) pertaining to the payload. Optionally, a Payload
object can be instantiated with a PayloadMeta object to ensure the originating
metadata (i.e., filename, source path, etc…) is also made available:
>>> import os
>>> from stoq.data_classes import PayloadMeta, Payload
>>> filename = '/tmp/test_file.exe'
>>> with open(filename, 'rb') as src:
... meta = PayloadMeta(
... extra_data={
... 'filename': os.path.basename(filename),
... 'source_dir': os.path.dirname(filename),
... }
... )
>>> payload = Payload(src.read(), meta)
Scan payload¶
There are two helper functions available for scanning a payload. If a dispatcher
plugin is not being used, then a worker plugin must be defined by passing the
add_start_dispatch argument. This tells stoQ to send the Payload object
to the specified worker plugins.
From raw bytes¶
If a Payload object has not been created yet, the content of the raw payload can
simply be passed to the Stoq.scan function. A Payload object will automatically
be created.:
>>> start_dispatch = ['yara']
>>> results = s.scan('raw bytes', add_start_dispatch=start_dispatch)
From Payload object¶
If a Payload object has already been instatiated, as detailed above, the
scan_payload function may be called:
>>> start_dispatch = ['yara']
>>> results = s.scan_payload(payload, add_start_dispatch=start_dispatch)
Save Results¶
Finally, results may be saved using the desired Connector plugin. stoQ stores
results from the framework as a StoqResponse object. The results will be saved
to all connector plugins that have been loaded. In this example, we will only load
the filedir plugin which will save the results to a specified directory.:
>>> connector = s.load_plugin('filedir')
>>> connector.save(results)
Split Results¶
In some cases it may be required to split results out individually. For example, when saving results to different indexes depending on plugin name, such as with ElasticSearch or Splunk.
>>> results = s.scan_payload(payload)
>>> results.split()
Reconstructing Subresponse Results¶
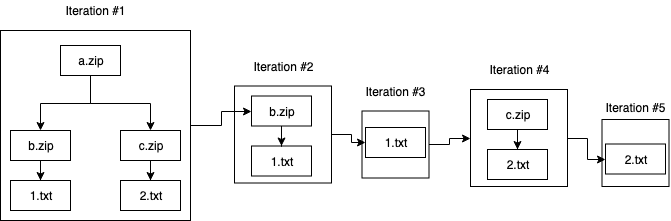
stoQ can produce complex results depending on the recursion depth and extracted payload objects. In order to help handle complex results and limit redundant processing of payloads when using stoQ as a framework, a method exists that will allow for iterating over each result as if it were the original root object. This is especially useful when handling compressed archives, such as zip or apk files that may have multiple levels of archived content. Additionally, the defined decorators will be run against each newly constructed StoqResponse and added to the results.
>>> for result in s.reconstruct_all_subresponses(results):
... print(result)
Below is a simple flow diagram of the iterated results when being reconstructed.
Multiple Plugin directories¶
When instantiating Stoq, multiple plugins directories may be defined. For more
information on default paths, please refer to the getting started documentation:
>>> from stoq import Stoq
>>> plugins_directories = ['/usr/local/stoq/plugins', '/home/.stoq/plugins']
>>> s = Stoq(plugin_dir_list=plugins_directories)
API¶
-
class
stoq.core.Stoq(base_dir=None, config_file=None, log_dir=<object object>, log_level=None, plugin_dir_list=None, plugin_opts=None, providers=None, source_archivers=None, dest_archivers=None, connectors=None, dispatchers=None, deep_dispatchers=None, decorators=None, always_dispatch=None, max_recursion=3, max_dispatch_passes=1)[source]¶ Core Stoq Class
Parameters: - base_dir (
Optional[str]) – Base directory for stoQ - config_file (
Optional[str]) – stoQ Configuration file - log_dir (
Optional[str]) – Path to log directory - log_level (
Optional[str]) – Log level for logging events - plugin_dir_list (
Optional[List[str]]) – Paths to search for stoQ plugins - plugin_opts (
Optional[Dict[str,Dict[~KT, ~VT]]]) – Plugin specific options that are passed once a plugin is loaded - providers (
Optional[List[str]]) – Provider plugins to be loaded and run for sending payloads to scan - source_archivers (
Optional[List[str]]) – Archiver plugins to be used for loading payloads for analysis - dest_archiver – Archiver plugins to be used for archiving payloads and extracted payloads
- connectors (
Optional[List[str]]) – Connectors to be loaded and run for saving results - dispatchers (
Optional[List[str]]) – Dispatcher plugins to be used - deep_dispatchers (
Optional[List[str]]) – Deep Dispatcher plugins to be used - decorators (
Optional[List[str]]) – Decorators to be used - always_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Plugins to always send payloads to, no matter what - max_recursion (
int) – Maximum level of recursion into a payload and extracted payloads - max_dispatch_passes (
int) – Maximum number of times the same payload will be deep dispatched
-
run(request_meta=None, add_start_dispatch=None, add_start_deep_dispatch=None)[source]¶ Run stoQ using a provider plugin to scan multiple files until exhaustion
Parameters: - request_meta (
Optional[RequestMeta]) – Metadata pertaining to the originating request - add_start_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Force first round of scanning to use specified plugins - add_start_deep_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Force second round of scanning to use specified plugins
Return type: None- request_meta (
-
scan(content, payload_meta=None, request_meta=None, add_start_dispatch=None, add_start_deep_dispatch=None, ratelimit=None)[source]¶ Wrapper for scan_payload that creates a Payload object from bytes
Parameters: - content (
bytes) – Raw bytes to be scanned - payload_meta (
Optional[PayloadMeta]) – Metadata pertaining to originating source - request_meta (
Optional[RequestMeta]) – Metadata pertaining to the originating request - add_start_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Force first round of scanning to use specified plugins - add_start_deep_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Force second round of scanning to use specified plugins - ratelimit (
Optional[str]) – Rate limit calls to scan
Returns: Complete scan results
Return type: StoqResponse
- content (
-
scan_payload(payload, request_meta=None, add_start_dispatch=None, add_start_deep_dispatch=None)[source]¶ Scan an individual payload
Parameters: - payload (
Payload) –Payloadobject of data to be scanned - request_meta (
Optional[RequestMeta]) – Metadata pertaining to the originating request - add_start_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Force first round of scanning to use specified plugins - add_start_deep_dispatch (
Optional[List[str]]) – Force second round of scanning to use specified plugins
Returns: Complete scan results
Return type: StoqResponse
- payload (
- base_dir (